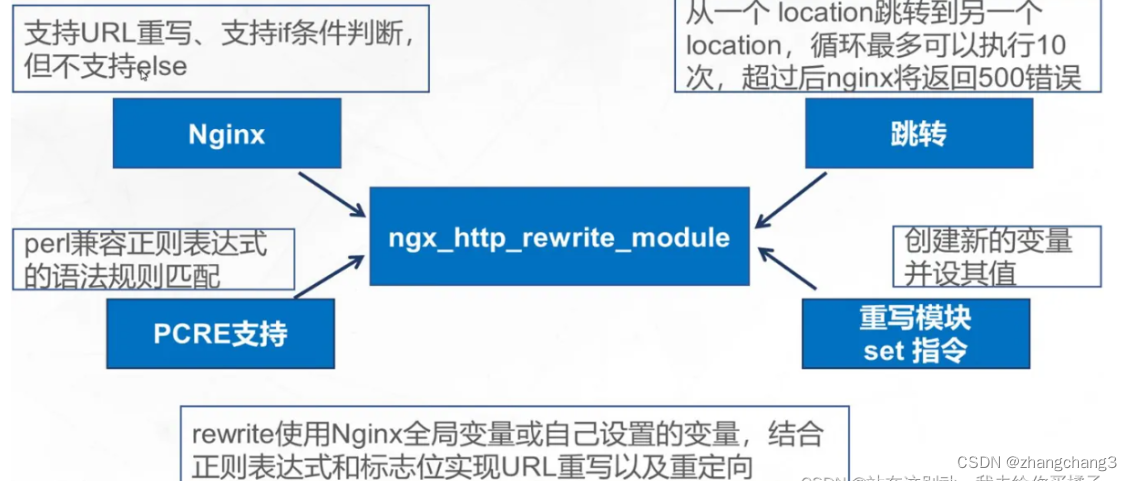
1. 两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 输出:[0,1] 解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6 输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6 输出:[0,1]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 104-109 <= nums[i] <= 109-109 <= target <= 109- 只会存在一个有效答案
进阶:你可以想出一个时间复杂度小于 O(n^2) 的算法吗?
我的答案:
暴力破解法:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize){
int i, j;
int* result = (int*)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
*returnSize = 2;
for(i = 0; i < numsSize - 1; i++){
for(j = i + 1; j < numsSize; j++){
if(nums[i] + nums[j] == target){
result[0] = i;
result[1] = j;
return result;
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
int main(){
int nums[] = {2, 7, 11, 15};
int target = 9;
int numsSize = sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0]);
int returnSize = 0;
int* result = twoSum(nums, numsSize, target, &returnSize);
if(result != NULL){
printf("[%d, %d]\n", result[0], result[1]);
free(result);
}
return 0;
}
哈希表解法:
C语言解法
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct hash_node {
int key;
int val;
struct hash_node* next;
};
struct hash_table {
struct hash_node** nodes;
int size;
};
struct hash_table* create_hash_table(int size) {
struct hash_table* table = (struct hash_table*)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_table));
table->nodes = (struct hash_node**)calloc(size, sizeof(struct hash_node*));
table->size = size;
return table;
}
void destroy_hash_table(struct hash_table* table) {
for (int i = 0; i < table->size; i++) {
struct hash_node* node = table->nodes[i];
while (node != NULL) {
struct hash_node* next = node->next;
free(node);
node = next;
}
}
free(table->nodes);
free(table);
}
int hash(int key, int size) {
return (key % size + size) % size;
}
void hash_table_put(struct hash_table* table, int key, int val) {
int idx = hash(key, table->size);
struct hash_node* node = table->nodes[idx];
while (node != NULL) {
if (node->key == key) {
node->val = val;
return;
}
node = node->next;
}
struct hash_node* new_node = (struct hash_node*)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_node));
new_node->key = key;
new_node->val = val;
new_node->next = table->nodes[idx];
table->nodes[idx] = new_node;
}
int hash_table_get(struct hash_table* table, int key) {
int idx = hash(key, table->size);
struct hash_node* node = table->nodes[idx];
while (node != NULL) {
if (node->key == key) {
return node->val;
}
node = node->next;
}
return -1;
}
int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize) {
struct hash_table* table = create_hash_table(numsSize);
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
int j = hash_table_get(table, complement);
if (j != -1) {
int* result = (int*)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
result[0] = j;
result[1] = i;
destroy_hash_table(table);
*returnSize = 2;
return result;
}
hash_table_put(table, nums[i], i);
}
destroy_hash_table(table);
*returnSize = 0;
return NULL;
}
int main() {
int nums[] = {2, 7, 11, 15};
int target = 9;
int returnSize;
int* result = twoSum(nums, 4, target, &returnSize);
if (result != NULL) {
printf("[%d, %d]\n", result[0], result[1]);
free(result);
}
return 0;
}
C++解法:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int, int> hashTable;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
if (hashTable.count(complement)) {
return {hashTable[complement], i};
}
hashTable[nums[i]] = i;
}
return {};
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {2, 7, 11, 15};
int target = 9;
vector<int> result = twoSum(nums, target);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
C和C++实现时的区别:
该代码与之前使用C语言实现的代码类似,也是通过遍历数组和使用哈希表来查找两个数之和等于目标值的下标。不同的是,该代码使用了C++的vector和unordered_map来实现,更加方便和易读。
什么是哈希表?
哈希表(Hash Table)是一种基于哈希函数(Hash Function)实现的数据结构,用于支持快速的插入、删除、查找操作。它的核心思想是通过将元素的关键字映射为一个索引(即哈希值),将元素存储在数组中对应索引的位置上,从而实现快速查找的目的。
哈希表包括两个基本操作:插入和查找。对于插入操作,我们首先计算出待插入元素的哈希值,然后将元素存储在哈希值对应的位置上;对于查找操作,我们先计算出目标元素的哈希值,然后在哈希表中查找是否存在该元素。
哈希表的优点是可以实现快速的插入、删除、查找操作,时间复杂度为O(1)(在哈希函数的选择、哈希冲突的处理等方面有影响)。缺点是在处理哈希冲突时需要额外的时间和空间成本,并且哈希函数的选择对哈希表的性能影响很大。
解析:
哈希表能够降低这个题目的时间复杂度的原因在于,哈希表的查找操作的时间复杂度为O(1),因此可以通过将每个元素的值作为哈希表的键,将每个元素的下标作为哈希表的值,来加速查找过程。
具体地,对于给定的目标值target和数组nums,我们可以遍历一遍数组nums,在遍历的过程中,对于每个元素nums[i],我们计算出其与目标值的差值complement=target-nums[i],然后在哈希表中查找是否存在该差值。如果存在,说明我们已经找到了两个数之和为目标值target,可以直接返回它们的下标;否则,将当前元素nums[i]插入到哈希表中,继续遍历数组。
由于哈希表的查找操作的时间复杂度为O(1),因此总时间复杂度为O(n)。相比于暴力枚举的O(n^2)时间复杂度,哈希表能够显著地降低时间复杂度,提高程序的效率。
反思总结:
从这个题目我们可以学到以下几个方面的知识和技能:
-
编程语言的基本语法和使用:这个题目需要使用C语言实现,因此需要熟悉C语言的基本语法和常用的函数库。
-
实践能力的提升:这个题目需要我们将理论知识转化为实践能力,因此需要多做练习,提高编程实践能力。
总之,这个题目可以帮助我们加深对数据结构与算法、编程语言和问题解决思路的理解和掌握,提高实践能力和解决实际问题的能力。